Table Of Content

Validity refers to whether or not a test or experiment accurately measures what it claims to measure. If the final group of participants doesn't represent the larger group accurately, generalizing the study's conclusions is difficult. Organizational research, for example, employs longitudinal research to identify how people in the workplace or other similar settings interact with each other. This kind of research is useful for understanding how rapport is established and whether productivity increases as a result.
How to Plan a Longitudinal Study?
In contrast to longitudinal quantitative methodologies LQR focuses on individual narratives and trajectories and can capture critical moments and processes involved in change. Saldana [3] identifies the principles that underpin LQR as duration, time and change and emphasizes that time and change are contextual and may transform during the course of a study. The attrition in the sample highlights the complexity of having a heterogeneous sample in longitudinal research. We were well aware at the outset of the different disease trajectories of the tumor groups but for the purposes of analysis we designed the data collection points to be the same for all patients.
New data
For this reason we do consider that this paper will have particular relevance for researchers interested in chronic and life limiting conditions. We wished to interview patients shortly after diagnosis, which is a critical point in the patient pathway. Sensitive recruitment of participants soon after a life changing diagnosis, such as cancer, is important in building relationships and establishing a long term commitment to a study. Although building relationships and developing trust is essential this adds complexity to the role of the researcher involved in longitudinal research.
Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study - BMC Medical Research Methodology - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Qualitative longitudinal research in health research: a method study - BMC Medical Research Methodology.
Posted: Sat, 01 Oct 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The Typical Longitudinal Study
Cost – compared to cross-sectional studies, longitudinal studies are typically substantially more expensive to execute, as they require maintained effort over a long period of time. Order – longitudinal studies reveal the order in which things happened, which helps a lot when you’re trying to understand causation. For example, if you’re trying to understand whether X causes Y or Y causes X, it’s essential to understand which one comes first (which a cross-sectional study cannot tell you). If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably feeling a bit overwhelmed by all the technical lingo that’s hitting you.

As members of the core research team we felt that we had developed a great deal of experience in the development and management of such a project. We felt that if we pooled our knowledge we could suggest some important lessons learned from our experience. The authors met at regular intervals to identify the key aspects of the researchers’ experience of conducting this LQR project that we considered were not well addressed within the current literature.
Visualize Trends Over Time
One-year longitudinal study of the stratum corneum proteome of retinol and all-trans-retinoic acid treated human skin ... - Nature.com
One-year longitudinal study of the stratum corneum proteome of retinol and all-trans-retinoic acid treated human skin ....
Posted: Tue, 11 Jul 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
When researchers pursue a short-term longitudinal study, then they are looking for answers to very specific questions. If a long-term model is developed, there is an opportunity to identify specific developmental trends that occur in various fields, including sociology, psychology, and general medicine. When they are observational, then longitudinal studies are able to observe the world without manipulating it in any way. That means they may have less power to detect casual relationships that may form in their observed subjects. Because there are repeated observations performed at the individual level with this option, there is also more power than other studies to remove time-invariant differences while review the temporal order of events that occur. • We have clearly identified that longitudinal research with patients with a poor prognosis and experiencing long term challenges is worthwhile.
Insights over time
With ever-growing computational abilities, the repertoire of statistical tests is ever expanding. In depth understanding and appropriate selection is increasingly more important to ensure meaningful results. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Cloudflare Ray ID found at the bottom of this page. Case-control studies compare groups retrospectively and cannot be used to calculate relative risk.
During this longitudinal project we developed expertise in managing practical and ethical issues, tried different analysis strategies to look for alternative ways of examining data and understanding the experience of participants. There have been successes in the strategies we have used and areas in retrospect that we could have worked differently. These factors, together with researcher continuity, were important in helping to maintain good recruitment rates for participants with better health and survival rates throughout the study.
Health sciences
To better grasp the practical applications and diverse scope of longitudinal studies, let's delve into real-world examples from various fields. These examples highlight the versatility and impact of this research approach across different domains. Presenting your longitudinal data in a clear and informative manner is essential for conveying the underlying trends and patterns to your audience. Effectively communicating the results of your longitudinal study is crucial to ensure that your research has a meaningful impact.
They enable us to connect the dots, see the bigger picture, and make informed choices that impact our lives and society as a whole. This paper has highlighted specific methodological, practical and ethical issues identified in an LQR programme of research about experiences of symptoms in cancer patients in the first year after diagnosis. The study itself has highlighted useful insights into these experiences and allowed examination of data from multiple perspectives, but importantly has been an important learning opportunity of the research team. A panel study is a type of longitudinal study that involves collecting data from a fixed number of variables at regular but distant intervals.
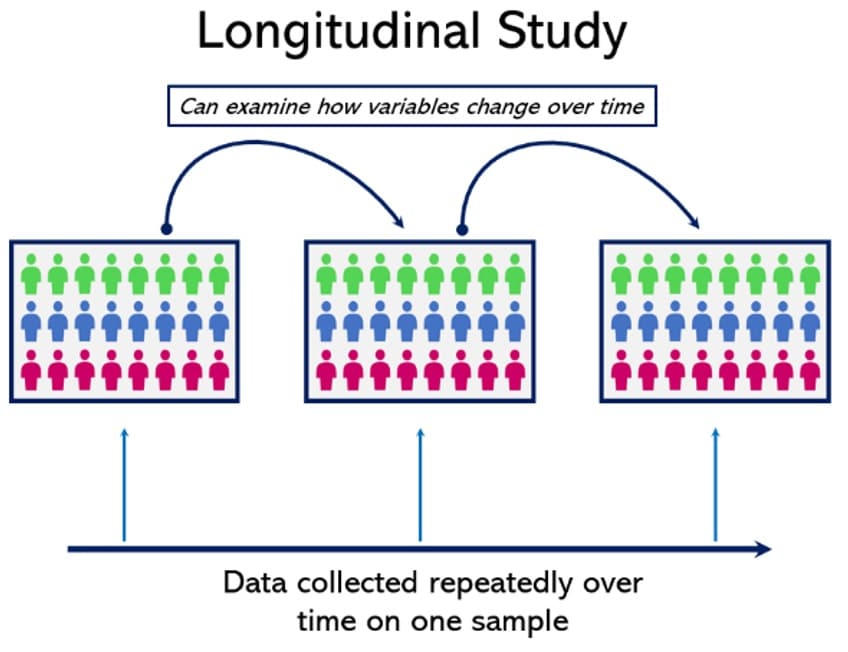
The advantage of this extended observation is that the researcher can witness the sequence of events leading to the changes in the traits of both the target population and the different groups. It can identify the causal factors for these changes and their long-term impact. Despite these potential pitfalls, you can still derive significant value from a well-designed longitudinal study by uncovering long-term patterns and relationships. The participants won't have recall bias if you use a prospective longitudinal study. Recall bias is an error that occurs in a study if respondents don't wholly or accurately recall the details of their actions, attitudes, or behaviors. Effectively analyzing longitudinal data allows you to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships that might have otherwise remained hidden.
This option looks at the past by reviewing historical information, such as medical records, to determine if there is a pattern in the data that is useful. Governmental and research institutes often carry out longitudinal studies and make the data available to the public. So you can pick up their previously researched data and use them for your own study. There are only two approaches you can take when performing a longitudinal study. During cohort study, the researcher exposes some group members to a specific characteristic or risk factor.
The choice of model depends on the hypotheses, timescale of measurements, age range covered, and other factors. Multilevel models are useful for hierarchically structured longitudinal data, with lower-level observations (e.g., repeated measures) nested within higher-level units (e.g., individuals). Overall, researchers need to test for and control cohort effects which could otherwise lead to invalid conclusions. Once you determine the type of longitudinal study you will conduct, you then must determine how, when, where, and on whom the data will be collected. The Harvard Study of Adult Development is one of the longest longitudinal studies to date. Researchers in this study have followed the same men group for over 80 years, observing psychosocial variables and biological processes for healthy aging and well-being in late life (see Harvard Second Generation Study).
In longitudinal studies, researchers do not manipulate any variables or interfere with the environment. Instead, they simply conduct observations on the same group of subjects over a period of time. We found that when seeking guidance for the project published literature was limited in highlighting debates about LQR focusing on the reporting of findings rather than developing debate about this emerging methodology. This paper has started to highlight some of the areas where further methodological exploration would be valuable.